Introducing Today’s Project!
In this project, I will demonstrate how to use Cloudfront to deliver a website globally. I’m doing this project to learn about CDNs and to setup the presentation tier of a three-tier architecture.
Tools and concepts
Services I used were include Amazon S3 and Amazon CloudFront. Key concepts I learnt include content delivery network (CDN), distributions, origin access control (OAC), performance load times, S3 Static Website Hosting vs CloudFront.
Project reflection
This project took me approximately an hour and a half. The most challenging part was probably understanding Origin Access Control. It was most rewarding to compare performance load times and understanding how CloudFront can be useful.
I chose to do this project today because I wanted to learn about CloudFront.
Set Up S3 and Website Files
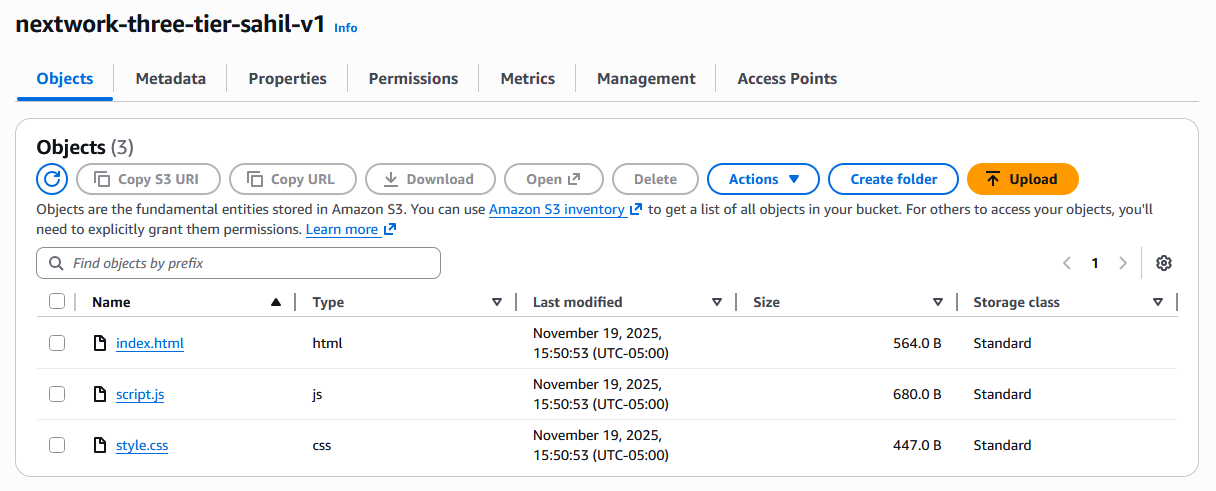
I started the project by creating an S3 bucket to store my website files. I can’t use CloudFront for this task because CloudFront is not a storage service, it’s a CDN service for objects that are already stored somewhere else.
The three files that make up my website are index.html, which is the main file for a website. It’s where you organize the text, pictures, and everything that makes up your webpage. style.css defines your website’s look, controlling fonts, colors, and layout for a consistent design and script.js is a JavaScript file that powers your website’s interactivity, controlling how elements react to user actions like clicks and form submissions.
I validated that my website files work by opening each file in a browser and visually inspecting it and making sure there are no errors.
Exploring Amazon CloudFront
Amazon CloudFront is a content delivery network, which means it caches static and dynamic content (i.e website files) to locations/servers around the world. Businesses and developers use CloudFront because it speeds up their website performance.
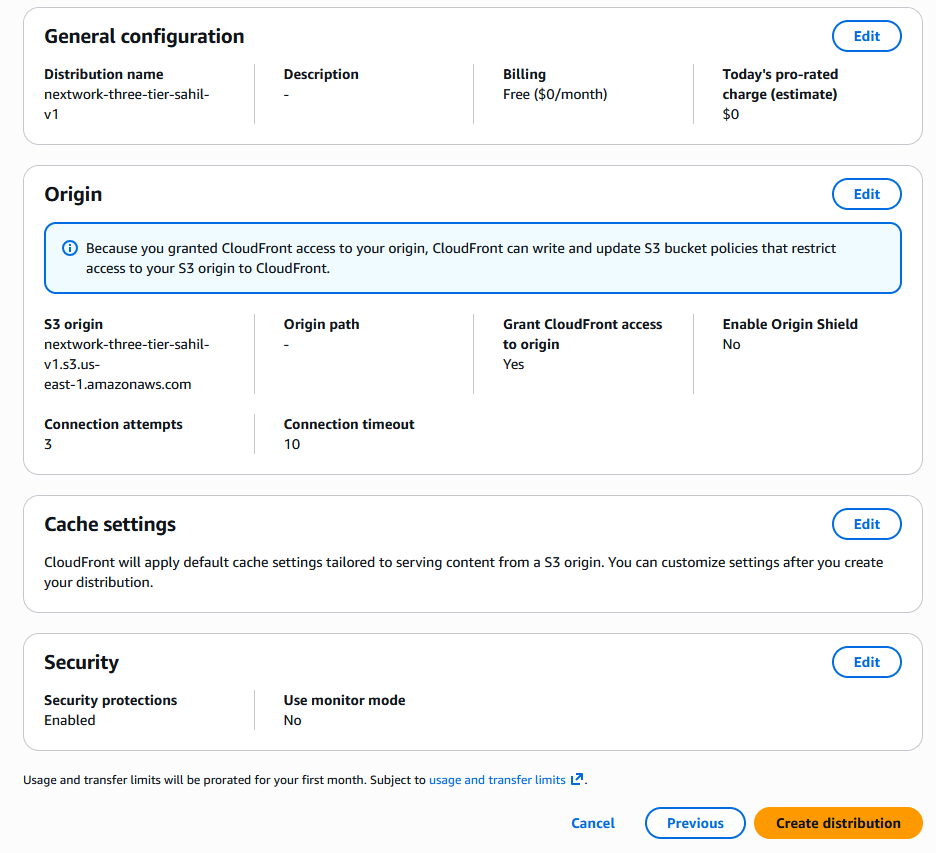
To use Amazon CloudFront, you set up distributions, which are instructions that tell CloudFront how to deliver the content. I set up a distribution for my website and the origin is my S3 bucket.
My CloudFront distribution’s default root object is index.html. This means when users visit my website root url, they will see the content described in index.html
Handling Access Issues
When I tried visiting my distributed website, I ran into an access denied error because Origin Access Control was note enabled to give CloudFront access to the S3 bucket.
My distribution’s origin access settings were set to Public. I changed the setting to Origin Access control settings.
To resolve the error, I set up origin access control (OAC). OAC is special user that is created to connect S3 with CloudFront - to give CloudFront access to S3, while still keeping the bucket restricted to public access. This improves security for the objects inside the S3 bucket.
Updating S3 Permissions
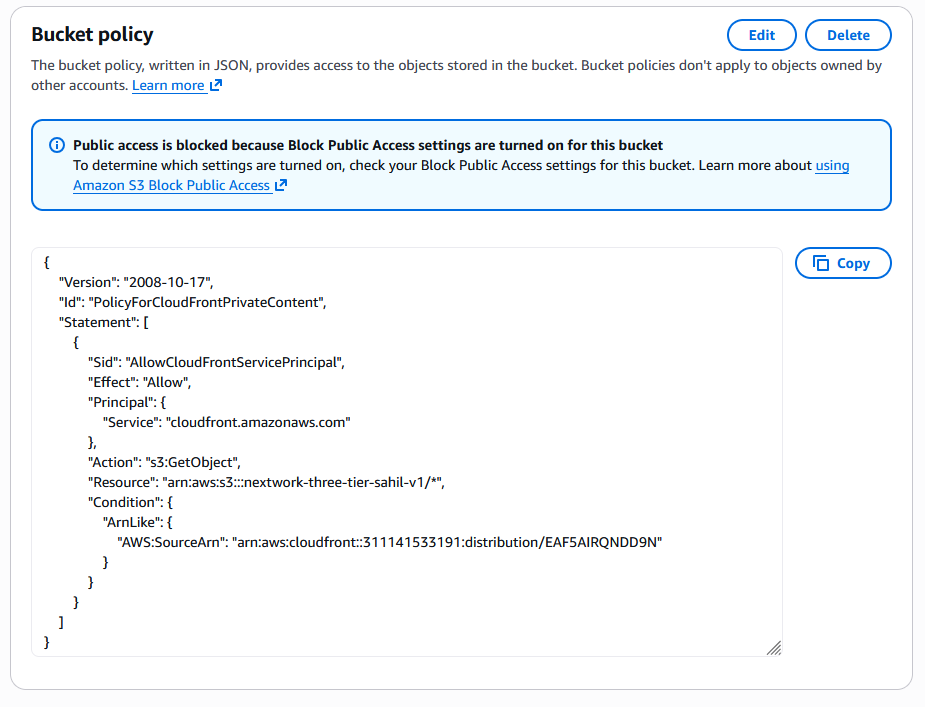
Once I set up my OAC, I did not need to update my S3 bucket policy.
Creating an OAC automatically gives me a policy I could copy, which grants CloudFront access to the objects inside the S3 bucket I created.
S3 vs CloudFront for Hosting
For my project extension, I’m comparing S3 with CloudFront. I initially had an error with static website hosting because I enabled S3 static website hosting without making my objects publicly available.
I tried resolving this by turning off ‘Block Public Access’ and I still ran into an error because bucket policy still does not allow public access to the objects.
I could finally see my S3 hosted website when I updated the bucket policy to allow proper public access to the objects inside the S3 bucket. This worked because the previous bucket policy only allowed CloudFront access to the S3 objects.
Compared to the permission settings for my CloudFront distribution, using S3 meant I had to enable public access to my bucket. I preferred using CloudFront because it meant bucket access is restricted to CloudFront only which is important for security.
S3 vs CloudFront Load Times
Load time means how long it takes for our browser to receive the requested content and display it to the user. The load times for the CloudFront site were faster than the S3 site because content is cached from edge locations.
A business would prefer CloudFront when performance/loads times are important to them. S3 static website hosting might be sufficient when you are hosting a simple website without performance/load time requirements.